Boron compounds attracted attention long before chemists named and purified them. Early civilizations put borates to work in glassmaking, pottery, and metallurgy, but it wasn’t until the 20th century that the link between boron intake and plant health pushed scientists to dig deeper. The path from raw mineral to specialized compounds was anything but easy. Chemists wanted to find boron forms that dissolved in water, stayed bioavailable in the body, and didn’t break the bank to produce. Boron citrate rose from those efforts, combining the benefits of boron with the better absorption seen with organic acid salts. Researchers worked not just to isolate this molecule, but also to understand its stability and compatibility with other nutrients. Looking back, the evolution of boron citrate followed close behind that of nutritional science itself. As attitudes toward mineral supplementation shifted, markets responded with refined, standardized forms and closer scrutiny on safety.
Boron citrate brings together boron—an essential trace element—and citric acid. The pairing creates a compound that sits in a sweet spot between solubility and stability, making it a favorite for dietary supplements and specialty formulations. Consumers looking for bone health support or hormone modulation don’t need to swallow large pills or deal with metallic aftertastes. Manufacturers see value in the straightforward synthesis and reliable yields during production as well. Boron citrate comes as a fine white to off-white powder, nearly odorless, and with a mildly sour note from the citrate. It dissolves in water, fitting in both food-grade and pharmaceutical uses. Some producers add anti-caking agents for ease of handling, but pure forms don’t need complicated additives.
Scrutinizing boron citrate up close, the powder flows easily, with a loose particulate structure. Solubility sits at the higher end compared to some borates, clocking in at several grams per liter in water at room temperature. Boron content typically lands around three to seven percent by weight, depending on how much citric acid finds its way into the final product. The molecule remains stable up to about 100 degrees Celsius, past which the citrate backbone can begin to break down. Moisture sensitivity isn’t a major concern under normal storage but leaving it exposed too long can cause clumping. The compound doesn’t carry strong odors or colors, so it doesn’t affect the appearance or smell of tablets, capsules, or liquid blends.
Boron citrate destined for the supplement market needs to meet strict technical standards. Leading producers provide certificates of analysis showing batch purity over 98%, with heavy metals falling below limits set by FDA or EU guidelines—usually less than 10 ppm for lead, arsenic, and cadmium. Particle size often sits at D90 < 150 microns, allowing for smooth blending without dusting during mixing or filling. Typical labeling lists boron content, not just the overall compound weight, since regulators and doctors base recommendations on actual elemental boron delivered per dose. Labels must include serving size, storage recommendations, source, and production origin. Clean-label trends encourage non-GMO sourcing and no unnecessary additives.
Synthesizing boron citrate starts with high-purity boric acid or a boron salt, which reacts with citric acid in water. Manufacturers control pH and temperature carefully, avoiding extremes that could break down the citrate groups or leave unreacted boron. The two ingredients mix until clear, creating a true solution. The water phase gets evaporated, either by gentle heating under vacuum or freeze-drying, to yield a crystalline or amorphous product. Quality checks focus on residual reagents, boron levels, and overall purity. Unlike more elaborate chelates, boron citrate production keeps steps direct. Multi-ton scales are common, given supplement industry demand. Whether processing in food or pharma settings, facilities follow GMP and maintain traceability back to the original boric acid batch.
Boron citrate doesn’t attract much interest for exotic chemistry, but it holds up well in solution. The major concern is hydrolysis at high temperatures or acidic conditions, which can free boric acid and citric acid. Storing in neutral pH and away from light helps preserve stability. Some producers experiment with alkali metal modifications—making sodium or potassium boron citrates—but pure boron citrate remains the workhorse in supplement lines. Analytical labs use techniques like ICP-MS or titration to check boron release, important for quality control and bioavailability claims. In rare applications, boron citrate serves as a precursor for boron-containing polymers or specialty ceramics, but most modifications focus on controlling solubility and purity.
Across the industry, boron citrate appears under a mix of names depending on the region or end-use. Common alternatives include boric citrate, boron tricitratoborate, and even “boron organic acid complex” in marketing literature. Supplement labels usually stick to “boron citrate” for simplicity and consumer recognition. Patent filings sometimes reference specific isomers or hydrate forms, but for most buyers the differences stay invisible. Large branded suppliers might add a trademarked name for their blend, linking it to clinical research or brand identity. International trade relies on clear chemical identifiers and batch-level documentation to avoid confusion between boron compounds with different safety or absorption profiles.
Handling boron citrate poses few real dangers compared to some other minerals. Dust generation during large-scale mixing can irritate eyes and lungs if proper ventilation or dust masks go unused. Ingesting massive amounts—well above safe daily limits—can cause gastrointestinal upset and, over the long haul, affect the kidneys or reproductive organs. Regulatory agencies set maximum tolerable intakes well above what labelled supplements provide. Workers in factories follow basic chemical hygiene, avoid eating in processing areas, and wash hands after handling. Production lines pass regular audits for GMP compliance, and trace contamination by heavy metals or solvents stays tightly controlled. Documentation and recall procedures ensure traceability in case of problems after the product hits shelves.
The market for boron citrate clusters in dietary supplements, where it supports bone strength, joint comfort, and hormonal balance. Nutritionists point to boron’s role in calcium and magnesium absorption, as well as its influence on enzymes involved in steroid metabolism. Pharmaceutical developers incorporate boron citrate into tablets, softgels, and gummies—partly for its stability, but also for consumer-friendly taste and appearance. Beyond human health, R&D teams have tested it in animal nutrition, slow-release fertilizers, and agricultural sprays, though these remain niche uses. The cosmetic sector has dabbled in adding boron citrate to creams and lotions based on theories around collagen support, but hard data in skincare remains limited. Some companies explore combinations with vitamin D, magnesium, or omega-3s in broad-spectrum bone health blends.
Clinical research continues to chip away at understanding where boron belongs in the nutritional toolbox. Investigators track outcomes for bone mineral density, cognitive health, and even hormone profiles in both men and women. Basic science labs explore how boron citrate interacts with protein kinases, signaling proteins, and antioxidant enzymes. Formulators run shelf-life studies to confirm how the compound holds up under different environmental conditions. Universities cross-check bioavailability against other boron salts, building a clearer picture of who benefits most—those with dietary shortfalls, high physical demands, or special medical needs. The knowledge gap persists around long-term impacts and dose ranges, so big-name supplement brands invest in proprietary trials. This evidence base will shape how doctors and nutritionists talk about boron for years to come.
Boron toxicity rarely crops up in the general population given natural intake levels, but animal research flags problems at much higher doses. Chronic overconsumption affects male fertility in rodents, with studies showing lower sperm counts and changes in organ weights. Rat experiments at doses far above human supplement levels link excessive boron to kidney changes and odd bone development. Reproductive and developmental research helps set safe upper limits, grounding regulatory guidance. For consumers without kidney disease or major health challenges, boron citrate used according to label directions falls well within established safety margins. Ongoing surveillance in supplement markets watches for unlabeled high-strength products.
Demand for functional minerals keeps climbing as more people take charge of their nutrition. Boron citrate sits well-positioned for expanded sales, driven by both aging populations and younger buyers tuned into bone and hormone health. Research continues to test its impact on inflammation, cognitive function, and athletic recovery, which could crack open broader markets—including sports nutrition and healthy aging clinics. Green chemistry developments target cleaner, lower-energy synthesis routes, and manufacturers experiment with combining boron citrate with probiotics or plant extracts. Regulatory clarity—especially around daily values and health claims—remains a challenge, but steady investment in R&D and consumer education looks poised to solidify boron citrate’s role both in supplements and beyond.
Boron pops up in everyday foods. Nuts, leafy greens, and even apples carry a light dose. On grocery lists, boron doesn’t grab attention like vitamin C or calcium, but it plays its own quiet supporting role for the body. When supplement companies bond boron with citrate—a friendlier form for absorption—they produce boron citrate, a supplement scooped up by people looking to fill nutritional gaps. My own curiosity came from reading a study linking trace minerals and bone strength, right after my mother broke her hip. That hit close to home, so I started looking harder at these “supporting actors” beyond the usual vitamins.
Boron strengthens bones by helping the body use calcium and magnesium. The U.S. National Institutes of Health point to small but consistent links between higher boron intake and better bone density. Research in Arthritis & Rheumatism (1994) showed that people with low levels had more joint discomfort. These findings made sense when I watched a friend in the supplement industry explain that people rarely get boron from multivitamins, even though it helps the body keep bones firm and joints less cranky.
Hormonal balance is another reason boron citrate has fans. It influences how our bodies use estrogen and testosterone. Older adults, especially women, sometimes look for ways to soften menopause symptoms beyond traditional hormone replacement therapies. A clinical study in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives (1998) linked higher boron intake to sustained estrogen activity—something which could boost both mood and bone health. To me, the take-home isn’t in miracle claims, but rather in small, consistent advantages from filling tiny mineral gaps that build up over years, especially as diets get more processed and farming strips minerals from soil.
Some studies print bold headlines about boron and sharper thinking. Research from the University of Sussex found that people with higher boron levels process information faster and stay more alert. I’ve noticed that on days when my minerals are balanced—thanks to whole foods and the occasional supplement—I don’t just have more energy; my mind feels less foggy. That nudge in focus doesn’t replace enough sleep or exercise, but it adds up for folks juggling work and family.
Boron’s effect on the immune system doesn’t get as much attention, but it can influence inflammation. Chronic inflammation connects closely with heart disease, diabetes, and some cancers. Keeping inflammation markers low makes a big difference for long-term health, especially in families like mine that have a history of auto-immune issues. Boron citrate won’t pull all the weight, but it’s another piece in the puzzle.
Experts warn that moderation comes first. Most adults only need about 1–3 milligrams a day. The Food and Nutrition Board sets the tolerable upper intake level for adults at 20 milligrams per day. Too much boron causes problems like stomach upset and headaches, so dosing low and sticking with food sources remains safest. For those considering supplements, talking to a doctor makes sense—especially for anyone pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking medication for hormones or bones.
Many health problems stem from years of small imbalances or missing nutrients. Boron citrate fills an overlooked need for many people. Food alone can usually cover the need, but with processed diets and produce from mineral-stripped soils, these small deficits show up more often, especially in those of us over 40. Solutions look like soil renewal practices, wider supplement education, and regular blood work to spot gaps before symptoms snowball. Making sure our plates stay colorful and whole, and double-checking with healthcare professionals, keeps boron—and many other quiet nutrients—doing their part in the background.
Boron doesn’t get much attention in daily nutrition talks, but it’s crucial. The body uses boron to help bones stay strong, keep hormones balanced, and even support the way we think and remember. People pick boron citrate as a supplement to fill in gaps left by food, hoping for stronger bones or smoother joint movement.
Boron occurs naturally in fruits, nuts, leafy greens, and coffee. These foods usually deliver about 1 to 3 mg per day to most adults. Supplementing pushes intake higher. Researchers have looked at amounts up to 20 mg per day for short stretches without big safety problems, but most people stick closer to 3 mg to 6 mg each day. This range matches the natural food supply and stays under the level where risks show up—reliable health authorities peg 20 mg as the top safe daily amount for adults. Going past this doesn’t give extra benefits and starts raising the risk for side effects like headache or stomach upset.
Getting the most from boron citrate means paying close attention to how the body handles it. I’ve seen how some people jump right into doses they’ve read about online, but more isn’t always better. For most adults, starting at or below 3 mg daily covers needs without real risk. The body absorbs boron fairly easily, and taking it with food helps sidestep any stomach issues. Skipping meals with supplements can make absorption spotty and lead to more discomfort.
Boron can change the way certain medicines work, especially hormone therapies, blood thinners, or diabetes medications. Anyone considering boron citrate should check with a pharmacist or doctor if they use regular medications. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding need to be even more careful. Kids and teenagers have lower safety limits, so adult doses shouldn’t transfer to younger family members. In my own experience, talking to a healthcare professional before adding boron—or any supplement—always beats guessing.
Supplements aren’t watched as closely as medications, so picking a trusted brand goes a long way. Look for bottled supplements that show third-party testing for quality and list boron content on the label. Too many off-brand supplements underdeliver, or worse, pack in unsafe additives. Checking for a professional seal or a certificate of analysis helps avoid these problems.
Boron citrate doesn’t work miracles overnight. Bone strength, pain relief, or lower inflammation all take time, and good nutrition builds the foundation for these benefits. Supplements act as a boost for those whose diets come up short. Pairing boron intake with a diet rich in magnesium, calcium, and vitamin D creates the best setting for mineral and bone support. Lifestyle habits matter just as much—keeping active helps the body use nutrients, including boron, where they’re needed.
Go into any vitamin aisle, and a wall of bottles promises everything from stronger bones to sharper minds. Boron citrate sits on a shelf in that mix, often marketed for bone health, testosterone, and brain function. Still, every time a supplement gets popular, questions about safety show up just as fast. The reality often sits between wild internet claims and what most folks actually experience.
Boron is a trace element, found in foods like nuts, avocados, and leafy greens. Most people get a small amount just by eating a varied diet. The conversation turns to boron citrate when people take it in capsules to chase specific health goals. The big question pops up: does more boron bring big benefits, or just unwanted effects?
A little boron in food rarely causes problems. Transition to supplements, and things change. While the human body can handle small quantities, higher amounts over longer periods test those limits. The National Institutes of Health notes that the safe upper limit for adults swings around 20 mg per day. Go past that for too long, and troubles appear.
Some who have gone overboard report stomach discomfort. Nausea, diarrhea, or a queasy gut are the early warning signs. It’s not unique to boron citrate, but people underestimate it. At higher doses, headaches and skin rash creep up. There are even cases where very large doses led to symptoms like tremors, confusion, or in rare cases, kidney issues and reproductive changes. Those headlines rarely show up, but the risks are real enough to give anyone pause.
Folks with kidney challenges or chronic illness might see harsher reactions, since their bodies don’t clear minerals as efficiently. Pregnancy calls for more caution. Some animal studies link excessive boron to developmental problems, so most doctors tell expectant mothers to avoid it outside regular diet.
Some research links boron to bone strength and hormone balance. Early trials hint at benefits for arthritis and possible testosterone boosts, but large human trials remain slim. Most of what’s out there are small studies or animal research, which can’t always be trusted to predict the real-world outcome for everyone.
Supplement makers sometimes run with the hopeful headlines, skipping over the actual science. Real peace of mind comes from knowing that long-term, high-dose safety just hasn’t been mapped out. Nutrition experts, including registered dietitians, recommend sticking with food-based sources or talking to your doctor before starting high-dose supplements.
Check labels. Many off-the-shelf boron citrate bottles peg a dose at two or three times what’s in a healthy diet. Pick products that tell you exactly what’s inside, preferably with third-party certifications. Anyone who tries something new and notices odd symptoms should stop immediately and let a healthcare professional know.
Doctors often ask about supplements during checkups, but people forget to mention them. Open conversations with your provider bring better safety and more effective solutions. Most people get enough boron from everyday foods. For those considering extra, it’s not worth chasing promises without checking the possible side effects.
Boron has been around the supplement aisle for a while, often taking the back seat to heavy hitters like magnesium and calcium. Boron citrate, in particular, comes up in conversations about bone health, hormone support, and athletic performance. With the popularity of biohacking and self-care routines, some folks are reaching for boron every day—without much thought about what happens over the years.
The human body holds on to only a tiny amount of boron. Researchers have found it playing a helpful role in bone metabolism, cognitive function, and reducing inflammation. Some studies done at respected institutions like Oregon State University point out that diets low in boron can lead to lower bone density and more joint pain, especially in older adults. Boron can also affect hormone balance, sometimes giving testosterone and estrogen a slight nudge.
You hear a lot about water-soluble versus fat-soluble vitamins. With boron, the kidneys step in and clear out what the body doesn’t need pretty easily. Most adults taking less than 3 milligrams each day don't run into trouble, according to the US National Institutes of Health. Multivitamins and food rarely get you past that.
Problems start when folks treat minerals like a quick fix and take high doses over months or years. Studies have shown that high intake (over 20 milligrams per day) can hurt kidney function, bring on digestive issues, and cause skin rashes. These are not theoretical risks—they show up in published case reports and hospital records. The European Food Safety Authority draws the line at around 10 milligrams daily for adults.
No long-term, large-scale clinical trials track people popping boron citrate supplements for decades. That’s a gap not just for boron, but for most nutrients. We know from animal studies and short-term trials that staying inside that 1-3 milligram sweet spot looks safe, and may even help with absorption of other minerals. Groups who pay attention to bone health—like postmenopausal women—get some encouragement from this, but still, it isn’t a green light to double or triple the dose without talking to a doctor.
Older adults and those with kidney issues run into trouble sooner. If kidneys stumble, excess boron hangs around, causing real problems. Keeping tabs with blood tests and talking honestly with doctors is critical.
The world of supplements can tempt anyone to push limits, thinking more is always better. Trusted brands should lay out exactly how much boron sits in each pill. Sticking to established guidelines—about 1-3 milligrams per day—is the way to play it safe, especially with long-term use.
People get a bit of boron from fruits, leafy veggies, and nuts, so most balanced diets cover daily needs. Before adding another pill, consider what’s already on your plate and talk strategy with a healthcare professional. If more studies come out and show long-term benefit or risk, then those recommendations might shift.
Paying attention to dosing, keeping lines open with medical providers, and remembering that a healthy diet covers most basics goes further than chasing new supplements. Boron citrate—like any mineral—works best as part of a bigger health picture, not a solo act.
Boron often flies under the radar compared to flashier minerals like magnesium or calcium. Plenty of supplements advertise boron citrate for bone strength, hormone balance, or as a boost for mental focus. Every so often, someone asks if boron risks clashing with medications or other supplements. It’s a fair question, especially for folks who juggle prescriptions, vitamins, or herbal blends.
After seeing patients in clinic settings experiment with supplement routines, one thing becomes clear: nothing works in isolation. Boron citrate doesn’t usually pop up as a troublemaker in drug interaction databases, but that doesn’t mean you get a free pass. Anybody who uses hormone-based prescriptions like estrogen, or drugs that influence calcium, needs real answers.
For those with arthritis, boron sometimes gets picked for joint health alongside NSAIDs. I’ve heard stories of folks feeling better, but science gives a mixed review, and there’s always concern about the cocktail effect. If someone takes blood thinners like warfarin, mixing in trace minerals—boron included—adds another variable. The changes probably aren’t huge in healthy adults, but people on narrow therapeutic index drugs should keep their doctor in the loop.
Walk into any health food store and you'll see an aisle loaded with minerals bottled next to each other. People often forget that high doses of calcium, magnesium, vitamin D, and boron might pile on a strain for kidneys, especially for anyone with underlying kidney disease. Boron helps bones use calcium and magnesium wisely. At first glance, it sounds like a good team-up, except too much could tip the balance, especially for people already taking a lot of multivitamins or those with parathyroid problems.
Zinc and boron sometimes find their way into testosterone-boosting blends. In my own experience, a few younger clients made their own supplement stacks without real guidance. Blood tests sometimes showed unexpected results. Oversupplementing can throw off mineral ratios or even mess with absorption rates. Fact: the National Institutes of Health recommends no more than 20 milligrams of boron per day for adults. Push past that, and side effects show up—nausea, digestive distress, or even hormone shifts.
Supplement makers aren't subject to the same strict rules as pharmaceutical companies. Labels sometimes promise more than they deliver. Real safety data comes from case reports, large studies, or ongoing user feedback.
Regulations vary around the world. In some places, you can buy boron off the shelf without so much as a warning label. Most doctors and pharmacists don’t get bombarded with boron-related emergencies, but that doesn’t dismiss the risk for people with chronic illness or polypharmacy situations. Between food sources and supplements, intake can sneak up unnoticed.
Checking in with a healthcare provider remains a smart move, especially before starting any new mineral or vitamin supplement. A pharmacist can help scan for potential overlaps with prescription meds. People managing osteoporosis, kidney disease, or complex medication schedules should take extra care.
More research may sort out the finer details on boron’s impact, but for now, moderation and honest conversations with your care team serve better than guesswork and supermarket impulse buys.
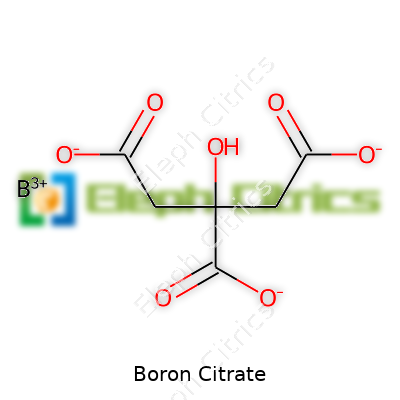
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | trihydroxy(trihydroxidooxy)boron |
| Other names |
Trisodium Boron Citrate Sodium Borate Citrate Boron Trisodium Citrate |
| Pronunciation | /ˈbɔːrɒn ˈsɪtreɪt/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | [85270-34-6] |
| Beilstein Reference | 3588631 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:132709 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL4297077 |
| ChemSpider | 21544330 |
| DrugBank | DB14536 |
| ECHA InfoCard | echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/infocards/100.128.962 |
| EC Number | 19139-60-5 |
| Gmelin Reference | 107164 |
| KEGG | C19329 |
| MeSH | D017940 |
| PubChem CID | 71425457 |
| RTECS number | EY2975000 |
| UNII | Z9K009ZC0A |
| UN number | UN2811 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C12H10B4O18 |
| Molar mass | 371.57 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 36.1 lb/ft³ |
| Solubility in water | Slightly soluble |
| log P | -1.09 |
| Acidity (pKa) | ~2.1, ~4.7, ~11.6 |
| Basicity (pKb) | pKb ≈ 12.8 |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.584 |
| Dipole moment | 6.39 D |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | V03AE02 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | May cause eye, skin, and respiratory tract irritation. |
| GHS labelling | GHS07, GHS08 |
| Pictograms | GHS07, GHS08 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | Hazard statements: Not a hazardous substance or mixture according to Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008. |
| Precautionary statements | Keep out of reach of children. If pregnant or nursing, consult your healthcare practitioner before use. Store in a cool, dry place. Do not use if seal is broken or missing. |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 1-0-0 |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose) of Boron Citrate: "2660 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| NIOSH | RN8220000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | 10 mg/m3 |
| REL (Recommended) | 3 mg |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | Not established |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Boric acid Boron glycinate Boron aspartate Boron gluconate Boron amino acid chelate Sodium tetraborate (Borax) Calcium borate Magnesium borate |