The industrial story of isobutyl lactate stretches back to a time when people looked for greener, more versatile solvents. As oil prices rose and stricter environmental rules shaped the chemical market, interest grew around lactate esters. The push for biodegradable, low-toxicity options put isobutyl lactate into sharper focus. It carved out a spot alongside its cousins like ethyl and butyl lactate, responding to heightened concern over air quality and operator health. Over the decades, refinements in fermentation and esterification have improved both quality and consistency. As consumer awareness sharpened around chemical residues and pollutants, isobutyl lactate gained new ground in multiple sectors, shaking off the earlier days when mineral spirits ruled without challenge.
Isobutyl lactate serves as an effective, biodegradable solvent with a fruity odor. Chemists appreciate its gentle solvency profile and value it as an alternative where toxic solvents create headaches. With a molecular formula of C7H14O3, its appeal comes from a balance between solvency power and a lower ecological footprint. You will spot it in personal care products, specialty coatings, and inks. Its use in flavor and fragrance blends points to its status as a safe and skin-friendly ingredient. Because it breaks down without creating hazardous byproducts, companies hoping to tighten up their sustainability claims often consider it over harsher agents.
Pour isobutyl lactate and you notice its clear to yellowish liquid state. Density hovers near 0.97 g/cm³ at room temperature, with a boiling point just below 170°C. Water solubility exists but remains moderate, marking the compound as amphiphilic—meaning it can mingle with both water and organic solvents. This makes it handy in applications like cleaning products, where switching between oil and water-based dirt is common. The ester functional group stands out, offering enough reactivity for chemical tweaking but remaining stable under standard storage. Its flash point provides safety in handling but should not lull people into careless storage.
Technical data sheets often list purity upwards of 98%, with water content kept low to avoid hydrolysis. Responsible suppliers publish details on residual acids, color index, and odor. Labeling under GHS frames isobutyl lactate as an irritant, mostly to eyes and skin, with recommendations for gloves and goggles in busy operations. Regulatory paperwork tracks content for food-grade uses and highlights environmental compliance for industrial runs. Proper packaging—usually in tight-sealed drums—prevents moisture pickup and product loss. Manufacturers supply certificates of analysis meeting local and international benchmarks, reflecting rising customer demands for transparency.
Making isobutyl lactate starts with natural or synthetic lactic acid as the backbone, paired with isobutanol in an acid-catalyzed esterification. This step pushes water out as a byproduct. Plants often draw feedstocks from cornstarch or sugar beet fermentation, reflecting renewed emphasis on sourcing from bio-based routes. With energy prices riding high and consumers scanning for cleaner labels, many producers turn toward greener catalysts and continuous-process reactors to boost yields and cut waste. Each batch gets tested for conversion and separated with distillation, trimming impurities to hit exacting downstream specs.
In the lab, isobutyl lactate responds well to hydrolysis, reverting back to lactic acid and isobutanol under acidic or basic conditions. This reversibility plays a role in chemistry classrooms and industrial recycling. The ester linkage can also absorb nucleophiles, allowing clever chemists to tweak the structure for specialty uses. Catalytic hydrogenation, oxidation, and even transesterification can yield modified versions for different industries. Each tweak shapes its polarity, scent, volatility, or other functional traits, widening its footprint in markets from pharmaceuticals to agrochemicals.
Isobutyl lactate appears under names such as 2-hydroxypropanoic acid isobutyl ester in technical lists. Trade catalogues often refer to it simply as isobutyl lactate, but you might also see it listed as lactic acid isobutyl ester depending on the supplier or intended market. Food additive registers may use an E-number system, driving home the overlap between chemical and food regulatory worlds. Identifiers like CAS numbers ensure clarity in cross-border commerce and help buyers avoid mix-ups with related compounds.
Handling isobutyl lactate in plant environments involves careful attention to PPE. Eye washes and vented storage areas become part of daily routines. Its irritant properties and flammability call for basic containment planning. Documentation from agencies like OSHA or ECHA urges routine checks of air quality and spill response readiness. In workplaces that encourage open conversation between floor workers and supervisors, near-misses and actual exposures get reported quickly, supporting a culture that values everyone’s safety. Regular drills and training sessions keep knowledge fresh.
You can see isobutyl lactate earn its keep in coatings and paints by cutting strong odors and enhancing spread. Printers value it as a plasticizer, where it boosts adhesion and print clarity. Chemists in household and personal care products like its mildness, which makes it fit for surface cleaners and body lotions. In food manufacturing, food-safe grades create fruity undertones in flavors and fragrances without leaving behind worrisome residues. R&D teams in biotech and pharma spaces look for non-reactive solvents to run extraction and purification campaigns—an area where isobutyl lactate stands out for its low toxicity and process stability.
Teams in academia and industry work driven by strong interest in renewable source esters, and isobutyl lactate gets plenty of bench time. Topics on the table cover biocatalytic routes that shrink the carbon footprint and upcycle fermentation co-products. Some research focuses on expanding the molecule’s utility beyond solvents—experimenting with enantioselective syntheses or as a chiral building block for pharma intermediates. Academic partnerships and public funding—especially in regions trying to build circular economies—increase scrutiny of waste streams and look for process improvements to help local employers gain a competitive edge.
Studies on isobutyl lactate toxicity highlight its low acute toxicity in mammals. Eyes and skin might show short-term redness or irritation, but lethal effects come only with massive doses far above workplace exposures. Inhalation data remain sparse, so cautious operators keep their spaces ventilated. Chronic exposure data, while limited, so far suggest little threat of long-term harm when standard precautions govern its use. Environmental fate research points to ready biodegradability, breaking down quickly under standard soil and water conditions—offering a route to compliance with demanding chemical footprint limits.
Tougher VOC limits, resource scarcity, and shifting consumer tastes keep isobutyl lactate near the center of green chemistry trends. Progress in fermentation and process intensification promises both higher yields and lower prices, inviting more industries to take a second look at smaller solvent blends. Biotechnology creates pathways for unique parent compounds—designer lactate esters that lower environmental burdens even further. Regulatory pressure not only in North America and Europe, but in Asia-Pacific too, keeps the industry looking at cleaner, renewable-sourced options. Creative chemists continue to explore how chemical modifications can stretch isobutyl lactate’s portfolio, working with real-world partners to close the loop between lab work and sustainable production.
Isobutyl lactate doesn’t sound familiar to most people. It feels like something you’d only see in a chemistry classroom or stuck on a technical label. Yet, this clear, fruity-smelling liquid shows up in places we all rely on: factories making cleaners, companies crafting inks, and even fields where crop protection products get sprayed. Over the past decade, a search for safer chemicals has given this ester a spot in many toolkits.
Years ago, walking through the back of a print shop, the air sometimes seemed heavy—almost oily. That odor came from volatile solvents, not the best for workers or the planet. Isobutyl lactate stepped in as an option with a much gentler scent and less health risk. In cleaning products, it works because it easily breaks down greasy stains, ink smudges, or paint residues. Compared to heavy-duty petrochemicals, it offers similar power with a softer touch. The Environmental Protection Agency even recognizes chemicals like this as “safer choice” ingredients, which leaves people breathing easier (quite literally).
Despite its industrial uses, isobutyl lactate isn’t locked away in warehouses. Small amounts help companies improve flavors and scents in processed foods and beverages. It doesn’t belong in grandma’s recipe for apple pie, but food formulators turn to it for fruit-inspired notes, especially when natural extracts come up short. According to the Food and Drug Administration, trace quantities are considered food-safe when used according to strict guidelines.
Formulators often seek out solvents that don’t harm skin or the planet. Isobutyl lactate comes from lactic acid, which manufacturers can produce through fermentation. As a result, there’s real potential for “greener” sourcing—corn or sugarcane fields, not oil rigs. It breaks down in the environment without leaving a toxic mess, which helps companies meet tighter environmental rules.
People sometimes forget that pesticide and herbicide sprays need carriers to deliver their active ingredients. Isobutyl lactate plays that carrier role. Its properties let pesticides dissolve more evenly, improving the spray’s ability to stick. Farmers benefit, as the product covers more surface and reduces costly waste. Keeping these carriers safer also reduces health risks in rural communities.
Using isobutyl lactate isn’t perfect. It still comes with flammability risks, and skin exposure at higher doses may trigger irritation. Workers handling it wear gloves and use ventilation gear for good reason. Some claims about its benefits sometimes get a bit exaggerated—no single solvent delivers everything.
A push for safer chemicals only grows as more consumers wake up to health and climate issues. I’ve seen workplaces shift away from harsh agents, partly because engineers found substitutes like isobutyl lactate. The next step? Keep supporting research on better, safer sources—maybe bio-based options from waste products, not just crops. Stronger training and tighter rules can help, too. Solutions like these help keep industries running, people safer, and the air a little cleaner for all of us.
Isobutyl lactate keeps popping up in products. You’ll find it in some flavors, fragrances, and sometimes in cleaning agents. Companies pick it because it brings a fruity, pleasant smell and blends easily. Whenever a chemical ends up in finished goods, it makes sense to wonder about its safety, especially if you spot it on ingredient lists for items you use or eat.
Scientific bodies have dug into isobutyl lactate’s safety. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) marks it as “Generally Recognized as Safe” (GRAS) for use in food at low levels. Europe’s food safety watchdogs agree, allowing it as a flavoring. For years, toxicology reports haven’t shown cancer risks or birth defects at amounts considered normal in food or cosmetics. Skin allergy studies on people have shown very rare cases of irritation, usually at high concentrations unlikely to show up in everyday settings.
Animal studies, often the mainstay for chemical testing, used far bigger doses than you’d find in your diet or fragrances. Rats given huge amounts didn’t show troubling changes in organs or behavior. This doesn’t give a blank check, but it helps scientists estimate safe limits for humans.
Every chemical, no matter how gentle, has a limit. Concentrated isobutyl lactate, like any solvent, might cause skin or eye irritation. Workers handling drums of the stuff at factories have a higher risk than someone sniffing a scented candle or tasting a piece of candy. Accidental swallowing of large amounts isn’t an everyday concern for most people, but warnings keep this risk in view for kids and workers alike. Mix-ups in industrial settings—wrong labels or poor ventilation—boost the danger.
Most safety decisions rely on data collected over decades. Still, there’s always a need for fresh eyes and updated checks. Consumer habits change. Novel uses pop up. Trends show people favoring “natural,” but even natural ingredients should get regular review. Isobutyl lactate’s safety in food and skin contact looks strong, but combinations with other ingredients haven’t been studied as much outside specialty research circles. Unknown risks can slip in if new patterns of use pop up or if evidence builds over time about rare allergic reactions.
The safest approach is paying attention. Read ingredient lists, especially if you have known skin allergies or headache triggers. At work, proper gloves, eye protection, and good ventilation limit the chance of irritation or overexposure for folks mixing or using large quantities. Keeping chemicals out of kids’ reach never goes out of style.
Reporting odd symptoms after contact—rashes, breathing issues, or burning—matters. These reports help update safety guidelines. Consumer and worker safety stories lead to label updates, improved training, or ingredient swaps if patterns show up years later. That’s how health standards grow stronger, product by product.
Rules for safe levels in food and cosmetics should stay clear and enforced. Inspections and company training keep mistakes down. Companies could fund more studies or share their safety findings. Regulators can tighten checks as new uses come along, not just react after complaints. Open access to recent toxicology reviews would help both health professionals and curious customers make more confident choices.
Walk into any hardware aisle, and most heavy-duty cleaners rely on complex chemistry beneath the label. Isobutyl lactate fits into many of these formulas because it comes from renewable sources and tackles grease with less environmental baggage than older options. Years ago, harsher chemicals were the norm for graffiti and paint removal. Today, when janitors or maintenance crews want a liquid that cuts sticky residues, dissolves adhesives, and does not give off overwhelming fumes, this ingredient ranks high on the list. Its pleasant smell and its ability to break down oily messes without leaving harsh residues lend it value in janitorial products and specialty surface preparations.
Artists, automotive shops, and home remodelers deal with tough questions about solvents. Nobody wants paint that dries too fast or too slow, and they definitely don’t want to breathe caustic vapors. Isobutyl lactate delivers a unique solution, serving as a solvent in paints and coatings that offer better performance and lower toxicity. Many water-based paints struggle with drying; adding a bit of this ester smooths out brush marks and helps products lay flatter. In my experience in a small DIY studio, surfaces coated with isobutyl lactate-enhanced paint handled repeated cleaning without dulling. Large-scale manufacturers and local hobbyists alike lean into this chemistry for both the efficiency and the cleaner air.
The beauty industry keeps shifting toward gentle solutions, but effectiveness still matters. Isobutyl lactate shows up in some lotions, nail polish removers, and creams because it works as a mild solvent and a carrier for fragrances. Skin easily tolerates it compared to stronger chemicals. Back when I worked retail at a pharmacy, we always checked product ingredients for any harsh solvents. Brands with isobutyl lactate tended to get fewer returns from customers complaining about heady smells or skin irritation.
Companies formulating flavors turn to isobutyl lactate as a source of that subtle, green-fruity note you taste in some candies and beverages. Food packaging sometimes uses it in printing inks and coatings to ensure the food stays uncontaminated and fresh. That crossover—making sure contact with food remains safe—places a big responsibility on chemical suppliers to check purity and trace origins. Given industry oversight and food safety standards, isobutyl lactate must be produced with a much tighter margin. In the rare cases I have toured manufacturing spaces, attention to detail on every container reminded me how much rides on people’s trust.
Every industry using isobutyl lactate faces the reality of changing regulations and consumer demand for greener choices. Factories and labs already switch to plant-based feedstocks, moving away from fossil chemicals. This ester comes out on top for its lower toxicity, but more transparency in sourcing, recycling improvements, and even more efficient production could go further. Manufacturers with strong safety records, detailed disclosure on supply chains, and genuine investments in renewable chemistry set themselves up ahead of shifting consumer scepticism. The industries that push for those changes shape not just their own future, but also the air and water for communities that share their surroundings.
Isobutyl lactate has shown up across many industries, usually as a solvent in coatings, cleaners, flavors, and fragrances. Coming from the chemistry world myself, I’ve watched folks work with this compound for years. It smells a bit like green apple, but what jumps out to lab veterans is how easily it reacts to air, moisture, and temperature changes. Carelessness doesn’t go unnoticed — even a single container left open can fill a room with an odd odor for days.
Those handling isobutyl lactate quickly learn to respect its flammability. It can catch fire from common ignition sources if left unattended in a warm or unventilated space. Storing it near any spark-prone equipment or forgetting to close the lid isn’t just risky, it’s begging for trouble. Fire departments record many of their routine calls to sites that stacked flammable materials together without thinking twice.
A dry, cool storage room means a lot more than just comfort. Temperatures above 30°C aren’t good for this chemical. High heat speeds up the breakdown, which boosts pressure inside drums and bottles. Vapors build fast, especially when a hot week hits, straining seals and gaskets. I’ve seen containers left in direct sunlight warp or leak — wasted product, wasted money, and an unsightly safety report for the workplace. The best lesson? Keep it out of sunlight and away from heaters or radiators. Always.
Oxygen and humidity play villainous roles with isobutyl lactate. As soon as a little water sneaks in, hydrolysis starts, which means the compound splits, forming lactic acid and isobutanol. Not only does this ruin the batch’s purity, but you also end up with acidity climbing and unpleasant fumes filling the work zone. A simple leak in a seal can transform a month’s supply into waste. Some sites go as far as using desiccant packs or nitrogen blanketing to keep air and moisture out — a small investment that avoids major cleanup and product loss.
Metal drums or high-density polyethylene bottles have held up well for most companies. Avoiding rusty cans or worn plastic keeps the chemical uncontaminated. I remember a plant where switching to double-sealed caps cut bad batches in half practically overnight. Proper labels and regularly checking storage dates help; nobody wants to discover expired drums that need hazardous waste handling.
From a regulatory view, violations around chemical storage keep cropping up. Professional oversight, regular audits, and well-trained staff stop small mistakes from becoming headline news. Spills, fires, and air releases lead straight to fines, shutdowns, or worse. Plenty of accidents come from simple shortcuts — storing solvents with acids, blocking ventilation, or stacking containers too high.
Factories and warehouses work better with clear policies for chemical handling. Emergency kits near storage rooms, up-to-date material safety data sheets, and frequent refresher training keep workers sharp. No shortcut replaces a healthy respect for flammable and volatile liquids. Taking textbook guidelines and making them standard practice pays back in uptime, clean safety records, and steady supply.
Isobutyl lactate pops up in plenty of places: solvents, flavors, fragrances, sometimes even in cleaning agents. Anyone paying attention to what goes down the drain might wonder if this stuff breaks down naturally or lingers in rivers and soil. Being concerned is fair—you see stories all the time about chemicals piling up where they shouldn't.
Researchers and manufacturers often say isobutyl lactate biodegrades easily. The compound comes from lactic acid and isobutanol, both derived from renewable resources. Once it gets out into the environment, microbes chew it up. A study by the OECD classified it as readily biodegradable. That’s a science-y way of saying within a few weeks to a couple of months, most of it disappears when the right bacteria are around.
Contrast that with some synthetic solvents. Many of those hang around for years, causing headaches for water treatment plants and wildlife. I once spoke with a water quality technician about how certain chemicals put a real load on treatment systems. He pointed out that substances which break down quickly—like isobutyl lactate—aren’t the main culprits clogging up the works or poisoning fish.
Even though isobutyl lactate breaks down, there’s more to the story. Ask anyone living near a river with foamy banks—they care about more than just how fast chemicals fade. Toxicity comes into play. The research here gives some relief: isobutyl lactate shows low toxicity to aquatic life. It doesn’t come with the chronic toxicity warnings seen with some solvents.
Still, that doesn’t hand out a free pass. Volume matters. Massive spills or careless disposal could overwhelm natural degradation. In my own backyard, a local group tested streams near an old industrial site. Ordinary chemicals caused problems just because the doses got too high for microbes to handle. That’s true with almost anything, even biodegradable stuff.
Using isobutyl lactate in place of more hazardous solvents turns out to be a smart move. Green chemistry trends reward companies for picking ingredients with lower persistence and less toxicity, both to people and wildlife. Long-term, these choices make a dent in the scale of chemical pollution. I’ve noticed more brands calling out their use of biodegradable solvents in cleaning products, especially as shoppers ask about ingredients.
Here’s where people can nudge the process. Ask brands and manufacturers about how they source and use isobutyl lactate. Push for full transparency on environmental testing. It also helps to stay skeptical of greenwashing—from what I’ve seen, terms like “eco-friendly” don’t always line up with real impact unless companies publish the science behind their claims.
Laws and regulations help, too. Wastewater limits, labeling, and stricter rules on solvent disposal all contribute to keeping waterways and soil healthier.
Companies face increasing pressure to show their ingredients break down and don’t cause long-term harm. Isobutyl lactate checks some important boxes—it’s biodegradable and carries low toxicity—making it a better option than many traditional chemicals. Still, careful use, good science, and honest communication stay important. Everyone using or encountering these substances needs real, trustable info about what happens after products get washed away.
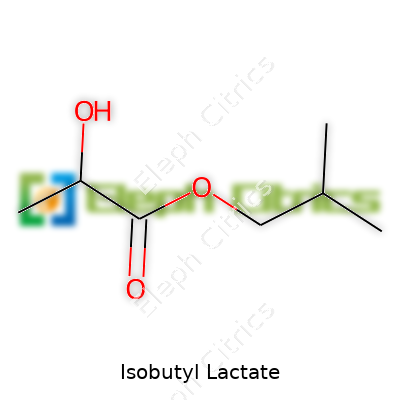
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | 2-methylpropyl 2-hydroxypropanoate |
| Other names |
2-Hydroxypropanoic acid isobutyl ester Isobutyl 2-hydroxypropanoate Isobutyllactate Isobutyl ester of lactic acid Lactic acid isobutyl ester |
| Pronunciation | /ˌaɪs.oʊˈbjuː.tɪl ˈlæk.teɪt/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 110-19-0 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Isobutyl Lactate JSmol 3D model (as string): ``` CC(C)COC(=O)C(O)C ``` This is the **SMILES** string format for Isobutyl Lactate, use it directly in JSmol or similar 3D viewers. |
| Beilstein Reference | 2418733 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:78376 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL3187443 |
| ChemSpider | 70300 |
| DrugBank | DB11248 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.093.739 |
| EC Number | 210-907-6 |
| Gmelin Reference | Gmelin Reference: **178210** |
| KEGG | C18694 |
| MeSH | D016617 |
| PubChem CID | 8095 |
| RTECS number | NJ3150000 |
| UNII | 96JNA1NSHN |
| UN number | UN3272 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID9020825 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C7H14O3 |
| Molar mass | 146.18 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear colorless liquid |
| Odor | Mild, fruity |
| Density | 0.868 g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | slightly soluble |
| log P | 0.58 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.3 mmHg (20 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | Isobutyl Lactate has a pKa of approximately 3.85 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -6.29×10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.4090 |
| Viscosity | 2.87 cP (25°C) |
| Dipole moment | 2.62 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 378.7 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -576.7 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -3275.7 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling | GHS02, GHS07 |
| Pictograms | GHS02,GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H315: Causes skin irritation. H319: Causes serious eye irritation. H335: May cause respiratory irritation. |
| Precautionary statements | Precautionary statements of Isobutyl Lactate: "P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P280, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | NFPA 704: 1-2-0 |
| Flash point | Flash point: 75°C |
| Autoignition temperature | 225 °C |
| Explosive limits | Upper: 5.4% ; Lower: 1% |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 (oral, rat): 8680 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): Oral rat 8700 mg/kg |
| NIOSH | WI9275000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | PEL (Permissible Exposure Limit) of Isobutyl Lactate: 5 mg/m³ |
| REL (Recommended) | 200 mg/L |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | 500 ppm |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Ethyl lactate Methyl lactate Butyl lactate Amyl lactate Propylene glycol Lactic acid |